Bash 命令实例
字典的用法
#!/bin/bash [ -z $1 ] && echo "$0 host disk" && exit 0 [ -z $2 ] && echo "$0 host disk" && exit 0 NODES='{ "192.168.30.19": [ "192.168.30.15", "192.168.30.16", "192.168.30.17", "192.168.30.18"], "192.168.30.18": [ "192.168.30.20", "192.168.30.40", "192.168.30.41", "192.168.30.45"] }' rhost=$(echo "$NODES" | jq -r --arg t "$1" 'to_entries[] | select(.value | contains([$t])) | .key') bad_host=$( $upssh $1 "df -h|awk '/$2/{print \"ps\",\"aux\",\"|\",\"grep\", \$NF}' | bash |awk -F'advertise-addr' '/tikv/{split(\$2,a,\" \");print a[1]}'" ) echo $bad_host
GNU核心命令/工具
rpm -ql coreutils
计算网络掩码
#!/bin/sh
get_mask () {
unset mask
while [ "$1" ]; do
bit=$(echo "obase=2;ibase=10;$1" |bc)
shift
mask="$mask$bit"
done
mask=${mask%%0*}
echo ${#mask}
}
maskpart=${@##*/}
echo "$(get_mask ${maskpart//./ })"
实例:
get_mask 255.255.255.240
计算网络地址
get_network () {
echo $@|awk 'BEGIN{FS="[./]";OFS="."} END{ print and($1,$5),and($2,$6),and($3,$7),and($4,$8)}'
}
start(){
eth0_IP1="122.224.104.20"
eth0_MK1="255.255.255.240"
eth0_GW1="122.224.104.17"
eth0_NET1=`get_network $eth0_IP1/$eth0_MK1`/`/usr/local/sbin/get_mask $eth0_MK1`
}
linux文件名中含有特殊字符'-'等特殊字符的解决方法
一般情况下,我们很少会遇到文件名中包含‘-’等这样的特殊字符。但是,我们从来不排除这个可能性。一旦有这样的情况发生,在使用一些命令对其进行处理的时候,因为‘-’后面的内容一般被解释为该命令的参数,这个时候就会提示命令出错。
例如:对一个名为‘-foo’的文件进行删除操作时
rm -- -foo rm ./-foo
养成好习惯,遇到不会用的命令,把阅读这些说明文档作为解决问题的第一步。
BASH/SHELL下的随机数
bash中的$RANDOM
echo $RANDOM
while读取变量
device1,deviceType,major,minor,permissions device2,deviceType,major,minor,permissions … … … deviceN,deviceTypeN,major,minor,permissions
#!/bin/bash [ $# -eq 0 ] && { echo "Usage: $0 filename"; exit 1; } while read line;do x=$IFS IFS=, ;read f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 <<<"$line" # quote fields if needed echo $f5 $f1 $f2 $f3 $f4 done < "$1" IFS=$x
Bash的输入输出重定向
基础知识
文件描述符(File Descriptor),用一个数字(通常为0-9)来表示一个文件。常用的文件描述符如下:
| 文件描述符 | 名称 | 常用缩写 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 标准输入 | stdin | 键盘 |
| 1 | 标准输出 | stdout | 屏幕 |
| 2 | 标准错误输出 | stderr | 屏幕 |
- 我们在简单地用<或>时,相当于使用 0< 或 1>(下面会详细介绍)。
- 管道“|”(pipe line),把上一个命令的 stdout 接到下一个命令的 stdin
- tee 命令的作用是在不影响原本 I/O 的情况下,将 stdout 复制一份到档案去
简单重定向
把cmd命令的输出重定向到文件file中。如果file已经存在,则清空原有文件,使用bash的noclobber选项可以防止复盖原有文件。
cmd > file
把cmd命令的输出重定向到文件file中,如果file已经存在,则把信息加在原有文件后面。
cmd >> file
使cmd命令从file读入
cmd < file
从命令行读取输入,直到一个与text相同的行结束。除非使用引号把输入括起来,此模式将对输入内容进行shell变量替换。
如果使用 «- ,则会忽略接下来输入行首的tab,结束行也可以是一堆tab再加上一个与text相同的内容,可以参考后面的例子。
cmd << text
把word(而不是文件word)和后面的换行作为输入提供给cmd。
cmd <<< word
以读写模式把文件file重定向到输入,文件file不会被破坏。仅当应用程序利用了这一特性时,它才是有意义的。
cmd <> file
功能同>,但即便在设置了noclobber时也会复盖file文件,注意用的是|而非一些书中说的!,目前仅在csh中仍沿用>!实现这一功能。
cmd >| file
使用文件描述符的重定向
使用文件描述符的重定向都使用了&符号。
cmd >&n 把输出送到文件描述符n cmd m>&n 把输出 到文件符m的信息重定向到文件描述符n cmd >&- 关闭标准输出 cmd <&n 输入来自文件描述符n cmd m<&n m来自文件描述各个n cmd <&- 关闭标准输入 cmd <&n- 移动输入文件描述符n而非复制它。(需要解释) cmd >&n- 移动输出文件描述符 n而非复制它。(需要解释)
注意:
>&实际上复制了文件描述符,这使得ls > dirlist 2>&1与ls 2>&1 > dirlist的效果不一样。 man bash的Redirection节中提及了这段内容。
重定向的组合应用
cmd 2>file 把文件描述符2重定向到file,即把错误输出存到file中。 cmd > file 2>&1 把标准错误重定向到标准输出,再重定向到file,即stderr和stdout都被输出到file中 cmd &> file 功能与上一个相同,更为简便的写法。 cmd >& file 功能仍与上一个相同。 cmd > f1 2>f2 把stdout重定向到f1,而把stderr重定向到f2 tee files 把stdout原样输出的同时,复制一份到files中。 tee files 把stderr和stdout都输出到files中,同时输出到屏幕。
Bash轻松获得网通电信地址段
#!/bin/sh FILE=/root/ip_apnic TMP=/dev/shm/ip.tmp rm -f $FILE wget http://ftp.apnic.net/apnic/stats/apnic/delegated-apnic-latest -O $FILE grep 'apnic|CN|ipv4|' $FILE | cut -f 4,5 -d'|'|sed -e 's/|/ /g' | while read ip cnt do echo $ip:$cnt mask=$(cat << EOF | bc | tail -1 pow=32; define log2(x) { if (x<=1) return (pow); pow--; return(log2(x/2)); } log2($cnt) EOF ) whois $ip@whois.apnic.net > $TMP.tmp sed -n '/^inetnum/,/source/p' $TMP.tmp | awk '(/mnt-/ || /netname/)' > $TMP NETNAME=`grep ^netname $TMP | sed -e 's/.*: \(.*\)/\1/g' | sed -e 's/-.*//g'|sed 's: ::g'` egrep -qi "(CNC|UNICOM|WASU|NBIP|CERNET|CHINAGBN|CHINACOMM|FibrLINK|BGCTVNET|DXTNET|CRTC)" $TMP if [ $? = 0 ];then echo $ip/$mask >> /root/CNC else egrep -qi "(CHINATELECOM|CHINANET)" $TMP if [ $? = 0 ];then echo $ip/$mask >> /root/CTC else sed -n '/^route/,/source/p' $TMP.tmp | awk '(/mnt-/ || /netname/)' > $TMP egrep -qi "(CNC|UNICOM|WASU|NBIP|CERNET|CHINAGBN|CHINACOMM|FibrLINK|BGCTVNET|DXTNET|CRTC)" $TMP if [ $? = 0 ];then echo $ip/$mask >> /root/CNC.1 else egrep -qi "(CHINATELECOM|CHINANET)" $TMP if [ $? = 0 ];then echo $ip/$mask >> /root/CTC.1 else echo "$ip/$mask $NETNAME" >> /root/OTHER fi fi fi fi done rm -rf $TMP $TMP.tmp
统计文章的字母出现频率
tr -c a-zA-Z ' ' < file | tr A-Z a-z | tr ' ' '\n' | sort | uniq -c | sort -n | less
编写选择式菜单栏
tvlist="Sport Music News"
select choice in $tvlist; do
case $choice in
Sport)
echo "Sport channel";;
Music)
echo "Music channel";;
News)
echo "News channel";;
*)
echo "Choose again";;
esac
done
自动vsftpd服务
#!/bin/sh USER="nobody" PASS="hzfj123(*&" start(){ echo "$PASS" | passwd --stdin $USER sed -r -i '/^nobody/s:/sbin/nologin:/bin/bash:g' /etc/passwd /etc/init.d/vsftpd start } stop(){ sed -r -i '/^nobody/s:/bin/bash:/sbin/nologin:g' /etc/passwd /etc/init.d/vsftpd stop } case "$1" in start) start;; stop) stop;; *) echo "$0 start|stop";; esac
快速修改nginx limit限速
#!/bin/sh CONFIG="/opt/nginx/conf/config/servers.conf" sed -r -i "s:conn_limit_per_ip .*:conn_limit_per_ip 10;:g" $CONFIG sed -r -i "s:req_limit_per_ip burst=.*:req_limit_per_ip burst=100 nodelay;:g" $CONFIG /etc/init.d/nginx reload
快速生成nginx_secure_link
#!/bin/sh FILE="/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/devil-150x150.png" EXPIRE=$(date +%s -d " December 18, 2012 15:35:00") URL="53kf@$FILE$EXPIRE" ST=$(/opt/php/bin/php -r "print str_replace(\"=\",\"\",strtr(base64_encode(md5(\"$URL\",TRUE)),\"+/\",\"-_\"));") LINK="http://1314i.us$FILE?st=$ST&e=$EXPIRE" echo $LINK wget $LINK
统计文本中出现的字符
[root@test html]# cat a abcdefg bcdefg cdefg defg efg fg g
[root@test html]# cat a | awk '{ len=length($0); for(i=1;i<=len;i++){ ch=substr($0, i, 1); print ch; } }' | sort | uniq a b c d e f g
同时,衍生出来统计一个文本文件里字符出现的次数
[root@test html]# cat a | awk '{ len=length($0); for(i=1;i<=len;i++){ ch=substr($0, i, 1); print ch; } }' | sort | uniq -c 1 a 2 b 3 c 4 d 5 e 6 f 7 g
由此可见,shell是强大的,无限的强大。
如何实现三层循环的脚本
要求
文件test内容类似如下: http://www.abc.com http://www.google.com
实现循环读这个文件,然后建立
abc.txt
google.txt
这样的文件
并在这些文件里写入
http://www.abc.com : www.abc.com
http://www.google.com: www.google.com
答案:
awk '{split($0,s,".");print $0" : "substr($0,8) > s[2]".txt"}' file
Telnet带验证的邮件发送
这段文字描述一下telnet发邮件的过程。在邮件排错中,通常用这种方式可以快速更容易的看到“返回信息”,来帮助管理员工作,同时也能更好理解邮件是如何交互应答。
telnet a.b.c.d 25 Trying a.b.c.d… Connected to a.b.c.d. Escape character is ‘^]’. 220 XXX SMTP System **HELO localhost** # 与服务器打招呼,并告知客户端使用的机器名字,可以随便填写 250 OK **AUTH LOGIN** # 使用身份认证登陆指令,如果这个指令返回“Send hello first”的错误,那么需要将上面的HELO改成EHLO重试登录 334 dXNlcm5hbWU6 **casDsdezMw==** # 输入已经base64_encode()过的用户名. base64加密字符可以google一下,输入明文就可以得到加密后的字符串 334 UGFzc3dvcmQ6 **MbSddwq3NQ==** # 输入已经base64_encode()过的密码 235 Authentication successful **MAIL FROM: test@test.com** # 告诉服务器发信人的地址,这里是test@test.com 250 Mail OK **RCPT TO: yourname@test.com** # 告诉服务器收信人的地址,这里是yourname@test.com 250 Mail OK **DATA** # 正面开始传输信件的内容,且最后要以只含有 . 的特殊行结束。 354 End data with . **To:yourname@test.com** **From:test@test.com** **Subject:test mail** **test body** **.** # 结束传输信件 **QUIT** # 退出服务器
随机点名抽奖代码
#!/bin/bash #功能描述(Description):随机点名抽奖器. #按Ctrl+C时:恢复光标,恢复终端属性,清屏,退出脚本. #防止程序意外中断导致的终端混乱. trap 'tput cnorm;stty $save_property;clear;exit' 2 #定义变量:人员列表文件名,文件的行数,屏幕的行数,屏幕的列数. name_file="name.txt" line_file=$(sed -n '$=' $name_file) line_screen=`tput lines` column_screen=`tput cols` #设置终端属性 save_property=$(stty -g) #保存当前终端所有属性. tput civis #关闭光标. #随机抽取一个人名(随机点名). while : do tmp=$(sed -n "$[RANDOM%line_file+1]p" $name_file) #随机获取文件的某一行人名. tput clear #清屏. tput cup $[line_screen/4] $[column_screen/4] echo -e "\033[3;5H 随机点名器(按P停止): " echo -e "\033[4;5H#############################" echo -e "\033[5;5H# #" echo -e "\033[6;5H#\t\t$tmp\t\t#" echo -e "\033[7;5H# #" echo -e "\033[8;5H#############################" sleep 0.1 stty -echo read -n1 -t0.1 input if [[ $input == "p" || $input == "P" ]];then break fi done tput cnorm #恢复光标. stty $save_property #恢复终端属性.
一句话备份文件到远端
tar -cvf - /tmp/testdir/ | gzip -c | ssh root@192.168.1.34 "cat > /tmp/testdir.tgz"
通过管道特性可以节省临时空间和时间
Bash比较语法
| 測試的標誌 | 代表意義 |
|---|---|
| -e | 該『檔名』是否存在?(常用) |
| -f | 該『檔名』是否為檔案(file)?(常用) |
| -d | 該『檔名』是否為目錄(directory)?(常用) |
| -b | 該『檔名』是否為一個 block device 裝置? |
| -c | 該『檔名』是否為一個 character device 裝置? |
| -S | 該『檔名』是否為一個 Socket 檔案? |
| -p | 該『檔名』是否為一個 FIFO (pipe) 檔案? |
| -L | 該『檔名』是否為一個連結檔? |
| -r | 偵測該檔名是否具有『可讀』的屬性? |
| -w | 偵測該檔名是否具有『可寫』的屬性? |
| -x | 偵測該檔名是否具有『可執行』的屬性? |
| -u | 偵測該檔名是否具有『SUID』的屬性? |
| -g | 偵測該檔名是否具有『SGID』的屬性? |
| -k | 偵測該檔名是否具有『Sticky bit』的屬性? |
| -s | 偵測該檔名是否為『非空白檔案』? |
| -nt (newer than) | 判斷 file1 是否比 file2 新 |
| -ot (older than) | 判斷 file1 是否比 file2 舊 |
| -ef | 判斷 file2 與 file2 是否為同一檔案,可用在判斷 hard link 的判定上。 主要意義在判定,兩個檔案是否均指向同一個 inode 哩! |
| -eq | 兩數值相等 (equal) |
| -ne | 兩數值不等 (not equal) |
| -gt n1 | 大於 n2 (greater than) |
| -lt n1 | 小於 n2 (less than) |
| -ge n1 | 大於等於 n2 (greater than or equal) |
| -le n1 | 小於等於 n2 (less than or equal) |
| test -z string | 判定字串是否為 0 ?若 string 為空字串,則為 true |
| test -n string | 判定字串是否非為 0 ?若 string 為空字串,則為 false。註: -n 亦可省略 |
| test str1 = str2 | 判定 str1 是否等於 str2 ,若相等,則回傳 true |
| test str1 != str2 | 判定 str1 是否不等於 str2 ,若相等,則回傳 false |
| -a (and) | 兩狀況同時成立!例如 test -r file -a -x file,則 file 同時具有 r 與 x 權限時,才回傳 true。 |
| -o (or) | 兩狀況任何一個成立!例如 test -r file -o -x file,則 file 具有 r 或 x 權限時,就可回傳 true。 |
| ! | 反相狀態,如 test ! -x file ,當 file 不具有 x 時,回傳 true |
执行结果变指令
#!/bin/bash ## A=100 ## ls -l ## free -m eval "`grep "^## " $0 | sed 's/^## //'`" echo "A=$A"
一条命令统计连接状态数
ss -antpl|awk '/^tcp/ {++state[$NF]} END{for(key in state) print key,"\t",state[key]}'
统计得到下面的连接结果,具体数字会有所不同:
LAST_ACK 1 SYN_RECV 14 ESTABLISHED 79 FIN_WAIT1 28 FIN_WAIT2 3 CLOSING 5 TIME_WAIT 1669
/^tcp/ 滤出tcp开头的记录,屏蔽udp, socket等无关记录。
state[] 相当于定义了一个名叫state的数组
NF 表示记录的字段数,如上所示的记录,NF等于6
$NF 表示某个字段的值,如上所示的记录,$NF也就是$6,表示第6个字段的值,也就是TIME_WAIT
state[$NF] 表示数组元素的值,如上所示的记录,就是state[TIME_WAIT]状态的连接数
++state[$NF] 表示把某个数加一,如上所示的记录,就是把state[TIME_WAIT]状态的连接数加一
END 表示在最后阶段要执行的命令
for(key in state) 遍历数组
print key,"\t",state[key] 打印数组的键和值,中间用\t制表符分割,美化一下。
一条指令将攻击IP阻挡
[root@Enter ~]# ss -an|grep TIME_WAIT|awk '{print $5}'|cut -d: -f1 | awk '{++S[$1]} END{for(a in S) if(S[a]>6) print a}'| xargs -i[] echo "iptables -I INPUT -s [] -j DROP"
统计CPU的使用率
#!/bin/bash SUM=0 for i in `vmstat -n 1 10 | grep -v ^p | awk '{ print $15 }' | grep -v "id"` do SUM=`expr $SUM + $i` done SUM=`expr $SUM / 10` BUSY=`expr 100 - $SUM` echo "$BUSY%"
- vmstat -n 1 10 取10次样本
- grep -v ^p 筛选去除第一项
- awk '{ print $15 }' 提取第15项数据(idle)
- grep -v “id” 去除标题栏
利用shell大量建立帐号
先建立一个纯文字档(userlist),里面存放着欲建立的user帐号,格式为 username:password,
user1:123456 user2:123456 user3:123456
编写shell script如下:
#!/bin/bash
FILE=$1
for i in `awk -F: '{ print $1 }' $FILE`
do
useradd $i
grep $i $FILE | cut -d":" -f2 | passwd --stdin $i
done
执行:
# ./mkuser.sh userlist
这样就可以大量创建帐号。
将 po 文件编译成 mo 文件
很多桌面应用程序都是是依靠 po 文件或 mo 文件来实现多语言版本。如果原作者提供了一个 po 文件或 mo 文件,那么我们就可以通过相关工具来自行汉化,或者翻译成其他语言版本。因为 mo 文件不能直接编辑,所以我们得编辑 po 文件,若仅有 mo 文件,那么就应该先把它转换成 po 文件后再进行编辑翻译。
po文件就是一个文本文件,那么如何将它编译成mo文件呢?而对于已经存在的mo文件,又如何将它反编译为po文件呢?
在linux下,可以用 msgfmt 命令将po编译成mo,而用 msgunfmt 将mo反编译成po文件。
用法举例如下:
将po编译为mo
msgfmt zh_CN.po -o zh_CN.mo
将mo翻译变为po
msgunfmt zh_CN.mo -o zh_CN.po
让history显示时间
一直以为history命令的输出不会有时间记录,今天看了history的man手册,才知道是自己孤陋寡闻了。
要想让history命令输出带有时期的格式,只需要设置HISTTIMEFORMAT环境变量就可以了,其时间格式描述和date命令是一致的,比如
#export HISTTIMEFORMAT=”%F %T ”
[root@localhost tools]# history 1 2007-03-27 11:18:40 rpm -qf /usr/sbin/lvscan 2 2007-03-27 11:18:40 sl 3 2007-03-27 11:18:40 ls 4 2007-03-27 11:18:40 df 5 2007-03-27 11:18:40 df -h 6 2007-03-27 11:18:40 cd /tmp
Linux上查看进程时间
可以用如下命令来查看:
ps axfo time,stime,start_time,start,pid,comm
bash计算网关地址
#!/bin/sh get_network () { echo $@ | awk 'BEGIN{FS="[./]";OFS="."} END{ print and($1,$5),and($2,$6),and($3,$7),and($4,$8) }' } get_broadcast () { echo $@ | awk 'BEGIN{FS="[./]";OFS="."} END{ print or($1,xor($5,255)),or($2,xor($6,255)),or($3,xor($7,255)),or($4,xor($8,255)) }' } get_network 61.164.42.20/255.255.255.240 get_network 192.168.18.254/255.255.255.0 get_broadcast 61.164.42.18/255.255.255.240 get_broadcast 192.168.18.254/255.255.255.0
bash计算网络掩码
255.255.255.0 -> 24
#!/bin/sh get_mask () { unset mask while [ "$1" ]; do bit=$(echo "obase=2;ibase=10;$1" |bc) shift mask="$mask$bit" done mask=${mask%%0*} echo ${#mask} } maskpart=${@##*/} echo "$(get_mask ${maskpart//./ })"
24 -> 255.255.255.0
#!/bin/bash all=(${@//[!0-9]/ }) [ "${#all[@]}" != "5" ] || echo ${@##*/} | grep -q '[^0-9]' && { echo "Usage: " echo "${0##*/} ip.ip.ip.ip/mask_bit" exit 1 } m_bit=${@##*/} [ "$m_bit" -gt 32 ] && { echo "Error: mask ($m_bit) is over range. maximum 32." exit 2 } ones=$((m_bit / 8)) one_mod=$((m_bit % 8)) zeros=$(((32 - m_bit) / 8)) [ "$ones" -ge 1 ] && { for ((i=1;i<=$ones;i++)); do left=$left.255 done } [ "$one_mod" -ge 1 ] && { for ((i=1;i<=$one_mod;i++)); do mid_one=${mid_one}1 done for ((i=1;i<=$((8 - one_mod));i++)); do mid_zero=${mid_zero}0 done middle=.$(echo "ibase=2;$mid_one$mid_zero" | bc) } [ "$zeros" -ge 1 ] && { for ((i=1;i<=$zeros;i++)); do right=$right.0 done } mask=$left$middle$right echo "${@%%/*}/${mask#.}"
如果安装了ipcalc工具,则使用下面的脚本
#!/bin/sh while read LINE;do rm -rf ip.tmp NET=`echo $LINE|awk -F: '{print $2}'|sed -r 's: ::g'` ipcalc $NET >> ip.tmp HOST=`grep Address ip.tmp|awk '{print $2}'` MASK=`grep Netmask ip.tmp|awk -F= '{print $1}'|awk -F: '{print $2}'|sed -r 's: ::g'` echo "vsftpd : $HOST/$MASK" done < ip.txt
计算网段内的主机起始和终止地址
#!/bin/sh ip_to_int() { IFS=. set -f set -- $1 REPLY=$(($1 << 24 | $2 << 16 | $3 << 8 | $4)) } int_to_ip() { REPLY=$(($1>>24)).$(($1>>16&0xff)).$(($1>>8&0xff)).$(($1&0xff)) } net=192.168.0.0 mask=255.255.0.0 ip_to_int "$net" && inet=$REPLY ip_to_int "$mask" && imask=$REPLY imin=$(($inet & $imask)) imax=$(($inet | $imask^0xffffffff)) int_to_ip "$imin" && min=$REPLY int_to_ip "$imax" && max=$REPLY printf 'min=%-15s (0x%08x)\nmax=%-15s (0x%08x)\n' "$min" "$imin" "$max" "$imax"
bash自动生成SSL-CRT证书
#!/bin/sh BAK=`date +%y%m%d%M%S` HOSTNAME="server" echo -n "Please Enter the domain name:" read DOMAIN mkdir -p /root/ssl/$DOMAIN DIR="/root/ssl/$DOMAIN" OPENSSL="/usr/bin/openssl" CONFFILE=/tmp/gencsr.$$ KEYFILE=$DIR/$HOSTNAME.key CSRFILE=$DIR/$HOSTNAME.csr CRTFILE=$DIR/$HOSTNAME.crt mkdir -p $DIR cat<<@eof This script generates a Certificate Signing Request for server $HOSTNAME It produces these two text files: $HOSTNAME.key the Private Key $HOSTNAME.csr the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) $HOSTNAME.crt the Certificate Result (CRT) @eof cat <<@eof > $CONFFILE [ req ] # openssl req params prompt = no distinguished_name = dn-params [ dn-params ] C = CN ST = Zhejiang O = Audividi OU = IT Dept L = HangZhou CN =$DOMAIN emailAddress = postmaster@audividi.com.cn @eof mkdir $DIR/$BAK mv $DIR/server.* $DIR/$BAK $OPENSSL genrsa 2048 > $KEYFILE $OPENSSL req -config $CONFFILE -new -key $KEYFILE -out $CSRFILE $OPENSSL req -x509 -days 365 -key $KEYFILE -in $CSRFILE > $CRTFILE2 rm -rf $CONFFILE rm -rf $CSRFILE
bash中的时间计算
现在时间 + 22:09:53 = 何时? 现在时间 + 128 分钟 = 何时?
#!/bin/bash # User Defined Variables # H,M,S 系统时间 # rhflag 0 = 当日, 1 = 明天, 2 = 后天... # strUsage 参数提示讯息 # timeoffset 使用者输入的时间 (时:分:秒) # oh,om,os 从 timeoffset 提列出来的 时, 分, 秒 (case 1) / 进位值 (case 2) # rh,rm,rs 运算结果 时, 分, 秒 # offset 使用 -h, -m, -s 参数时, 使用者带入的数值 # System Variables # $# 参数数量 # $0 Shell Script 档名 # $1 第一个参数 # $2 第二个参数 H=`date +%H` M=`date +%M` S=`date +%S` rhflag=0 strUsage="Usage:\n$0 hh:mm:ss\nor\n$0 [-h|-m|-s] number\n" case "$#" in 1) timeoffset=$1 oh=`echo $timeoffset | awk -F ':' '{print $1}'` om=`echo $timeoffset | awk -F ':' '{print $2}'` os=`echo $timeoffset | awk -F ':' '{print $3}'` rs=`expr $S + $os` if [ $rs -gt 59 ]; then ((rs -= 60)) om=`expr $om + 1` fi rm=`expr $M + $om` if [ $rm -gt 59 ]; then ((rm -= 60)) oh=`expr $oh + 1` fi rh=`expr $H + $oh` if [ $rh -gt 24 ]; then ((rhflag = rh / 24)) ((rh %= 24)) fi ;; 2) offset=$2 if [ $1 == "-h" ]; then rh=`expr $H + $offset` rm=$M rs=$S if [ $rh -gt 24 ]; then ((rhflag = rh / 24)) ((rh %= 24)) fi elif [ $1 == "-m" ]; then rh=$H rm=`expr $M + $offset` rs=$S if [ $rm -gt 59 ]; then ((oh = rm / 60)) ((rm %= 60)) rh=`expr $H + $oh` if [ $rh -gt 24 ]; then ((rhflag = rh / 24)) ((rh %= 24)) fi fi elif [ $1 == "-s" ]; then rh=$H rm=$M rs=`expr $S + $offset` if [ $rs -gt 59 ]; then ((om = rs / 60)) ((rs %= 60)) ((rm += om)) if [ $rm -gt 59 ]; then ((oh = rm / 60)) ((rm %= 60)) ((rh += oh)) if [ $rh -gt 24 ]; then ((rhflag = rh / 24)) ((rh %= 24)) fi fi fi else printf $strUsage exit 1 fi ;; *) printf $strUsage exit 1 ;; esac if [ $rh -eq 24 ]; then rh=0 rhflag=1 fi echo "$H:$M:$S" echo "$rhflag $rh:$rm:$rs"
执行实例
timeadd 22:09:53
14:52:10 (目前時間)
1 13:2:3 (明天下午一點零二分零三秒)
timeadd -m 128
14:53:52 (目前時間)
0 17:1:52 (今天下午五點零一分五十二秒)
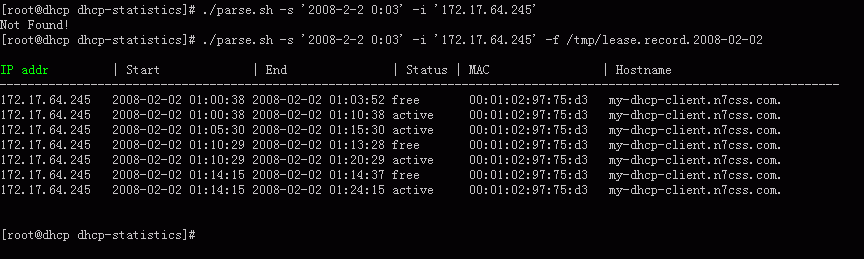
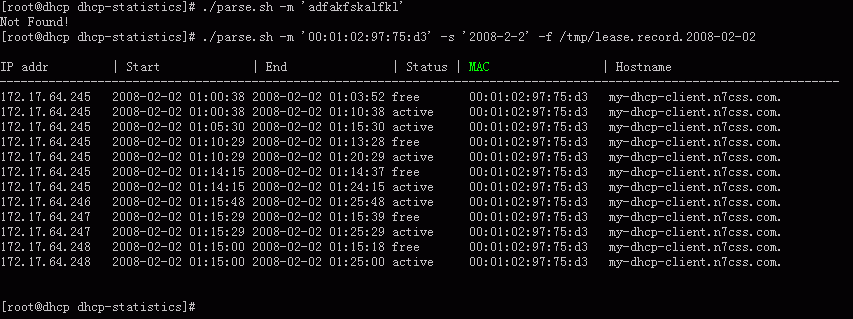
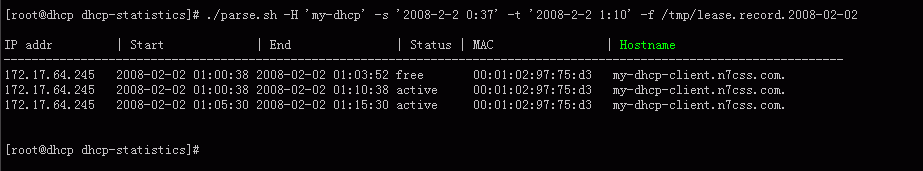
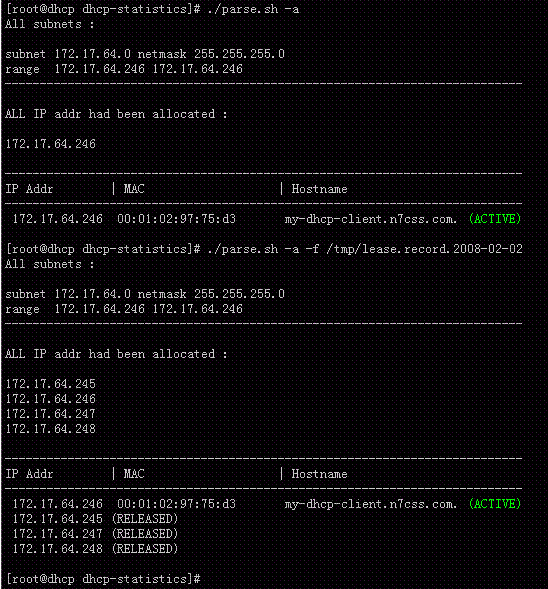
统计DHCP服务器ip分配的脚本
- 查询某个 mac 的租用记录 (v1.0)
- 查询某个 ip 地址的租用记录 (v1.0)
- 查询某个主机名的租用记录 (v1.0)
- 允许指定查询的开始时间和结束时间。开始时间默认为当天0点,结束时间默认为当前。(v1.0)
- 列出所有曾经被租用的 ip 以及它们目前的状态 (v1.0)
- 许指定某个备份的 lease.record.<date> 进行查询。(v1.1)
- 每月15日的0点10分自动把 lease 记录以 lease.record.<date> 备份,所以意味着默认只能查15天内的数据 (v1.1)
限制
目前暂时不考虑 DHCP Failover 以及 DHCP Omshell 的分析(这两个东西都会在 dhcpd.leases 中写数据)。
该脚本只记录客户机的 mac、客户机的主机名(如果有的话)以及 lease 的开始/结束时间/状态。
由于环境所限,只有1台客户机可供测试,所以欢迎各位朋友多多指正
脚本组成
a) lease_wath.sh ,主要是跟踪 /var/lib/dhcp/dhcpd.leases 文件的输出,并固定输出到某个文件(默认是 /tmp/lease.record)。
每次只能启动一个 leasewatch.sh ,否则程序会报错(Error!Another leasewatch is running!)
b) parse.sh :完成上述的功能的第1~6 项 。
c) rotate.sh :每月15日的0点10分自动把当前的 /tmp/lease.record 备份为 /tmp/lease.record.<date> ,同时重启 lease_watch。
屏幕截图
IP排序
MAC排序
HOSTNAME排序
列出所有曾经被租用的 ip 以及其状态 :
VidiNOW中的欢迎信息脚本
#!/bin/sh ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: Geminis <geminisshao@viatech.com.cn> # Copyright VIASOFEWARE Audividi VidiNow Corp. ### END INIT INFO # Define some variable for checking cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts HTTPD_PID="/var/run/httpd.pid" VERSION=`cat /etc/VidiNOW` SARAMON_FILE="/var/lock/subsys/saramonitor" TUNNEL_NUMS=`ps -e|grep tunnelserver|wc -l` INTERFACES=`grep -l 'ONBOOT=yes' ifcfg-eth*|sed 's/^ifcfg-//g'` GATE_DEV=`route -n|grep UG|awk '{print $8}'` show_netinfo(){ METHOD=`cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-$1|grep BOOTPROTO|awk -F= '{print $2}'` STATUS="inactive" COLOR="\\033[1;31m" # red color `ethtool $1|grep Link|grep -iq "yes"` [ $? == 0 ] && STATUS="active" if [ $STATUS == "active" ] && [ $1 == "$GATE_DEV" ];then COLOR="\\033[32;1m" # green color STATUS="*active" elif [ $STATUS == "active" ] && [ $1 != "$GATE_DEV" ];then TEMP_ROUTE=`ip ro|grep default|sed 's:\(.*\)eth.*:\1:'` COLOR="\\033[34;1m" # blue color # ip ro re $TEMP_ROUTE $1 # ip ro fl ca fi echo -en $COLOR if [ $METHOD == 'static' ];then IPADD=`cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-$1|grep IPADDR|awk -F= '{print $2}'` printf "\t\t%-5s(%s)\t\tIP: %-15s\n" $i $STATUS $IPADD else if [ -f /etc/dhcpc/dhcpcd-$1.info ];then IPADD=`cat /etc/dhcpc/dhcpcd-$1.info|grep IPADDR|awk -F= '{print $2}'` else IPADD="" fi printf "\t\t%-5s(%s)\t\tIP: %-15s\n" $i $STATUS $IPADD fi echo -en $"\\033[0;39m" } # Check network status and apache running and saramonitor status # if network is failure boot,the server will be reboot again # if apache isn't running , the server will be reboot again # if saramonitor is not run, the server will be reboot again echo -en $"\\033[33;1m" # yellow color echo " VidiNOW Meeting Center " echo " Powered by Audividi " echo " Version:$VERSION " echo " ---------------------------------------------------------------" echo -en $"\\033[0;39m" for i in $INTERFACES;do show_netinfo $i done echo -en $"\\033[33;1m" echo " ---------------------------------------------------------------" echo -en $"\\033[0;39m" # Check network status and apache running and saramonitor status # if network is failure boot,the server will be reboot again # if apache isn't running , the server will be reboot again # if saramonitor is not run, the server will be reboot again if [ ! -s $HTTPD_PID ]; then if [ -f /etc/failure ];then Failed_Num=`cat /etc/failure` Failed_Total=`cat /etc/allow_failure` if [ $Failed_Num -gt $Failed_Total ];then Failed_Num=`expr $Failed_Num + 1` echo $Failed_Num > /etc/failure /sbin/reboot else /usr/bin/cflag 1 [ -f /etc/failure ] && rm -rf /etc/failure >/dev/null 2>&1 & /sbin/reboot fi else echo '1'> /etc/failure /sbin/reboot fi else [ -f /etc/failure ] && rm -rf /etc/failure >/dev/null 2>&1 & fi
利用bash和perl发送邮件
Perl发送邮件代码
vi sendmail.pl
#!/usr/bin/perl -w use strict; sub usage() { print qq(usage: \"$0 [from:user] [to:user] [subject] < mailbody\"\n); } my $domain = "your.domain"; my($from,$rcpt,$subject); if (defined($ARGV[0])) { if ($ARGV[0] =~ qq(\@)) { $from = qq($ARGV[0]); } else { $from = qq($ARGV[0]\@$domain); } } else { usage(); exit 1; } if (defined($ARGV[1])) { if ($ARGV[1] =~ qq(\@)) { $rcpt = qq($ARGV[1]); } else { $rcpt = qq($ARGV[1]\@$domain); } } else { usage(); exit 1; } if (defined($ARGV[2])) { $subject = qq($ARGV[2]); } else { usage(); exit 1; } open(SENDMAIL, "| /usr/sbin/sendmail.sendmail -oi -t -f$from") || die qq(Cannot open sendmail output: $!\n); print SENDMAIL <<EOF; From: $from To: $rcpt Subject: $subject MIME-Version: 1.0 Content-Type: multipart/mixed; boundary="thisisatest" This is a multi-part message in MIME format. --thisisatest Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8 Content-Disposition: inline EOF while (<STDIN>) { print SENDMAIL; } print SENDMAIL <<EOF; --thisisatest-- EOF close (SENDMAIL);
生成附件的base编码包
vi attach.sh
#!/bin/sh filename=$(echo $1 | awk 'BEGIN{FS="/"}{print $NF}') realfile=$1 echo " --thisisatest Content-Type: application/octet-stream; name=\"${filename}\" Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=\"${filename}\" Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64 " base64 $realfile
使用方法
sendmail.pl 寄件者 收件者 主旨 键盘输入邮件内容 键盘输入邮件内容 键盘输入邮件内容 (Ctrl + D) sendmail.pl 寄件者 收件者 主旨 < 邮件内容档案 (cat 邮件内容档案; attach.sh 夹档1; attach.sh /path/to/夹档2) | sendmail.pl 寄件者 收件者 主旨 ps. 使用前记得先修改 sendmail.pl 裡面的 $domain 变数
举例说明
# adan 与 bob 都是本机帐号 sendmail.pl adan bob "This is a test" < mail.body # 寄给外部帐号 sendmail.pl adan someone@somewhere.com "This is a tes" < mail.body # 伪装寄件人 sendmail.pl billgates@microsoft.com someone@somwhere.com "This is a test" < mail.body # 夹带档案 (cat mail.body; attach.sh file1.txt; attach.sh file2.jpg) | sendmail.pl adan bob "This is a test" # 寄给本机所有使用者 (分别夹带不同档案)
#!/bin/sh if [ "$1" == "" ]; then echo "Usage: $0 outputfile" exit 1 elif [ -e "$1" ]; then true > $1 fi cd /home for i in *; do id $i > /dev/null 2>&1 if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo $i >> $1 fi done sh userlist_generator.sh /tmp/user_list.txt for i in $(cat /tmp/user_list.txt); do \ (cat mail.body; attach.sh file1.txt; attach.sh userfiles/$i.txt) | sendmail.pl root $i "公告" \ done
一次读取多行个变量
#!/bin/sh read -u 0 -d \n MODE MIP < /root/test echo "MODE=$MODE" echo "MASTERIP=$MIP"
cat /root/test 1 192.168.1.6
如何按IP地址排序
# sort -n -t. +0 -1 +1 -2 +2 -3 +3 -4 filetext
这是一个专门发代码的网站 代码上面自动带上颜色 蛮喜欢的 .. 做个记录 http://fayaa.com/code/view/3021/
Bash监控web服务器,并将报警发送到手机
#Author #1.change you phone number. #2.the program "sms" is fetion for linux. server_list=(192.168.0.21:80 192.168.203.1:80) date=`date +"%y%m%d-%H:%M:%S"` okmsg=/var/log/okmsg errormsg=/var/log/errormsg lockfile=/usr/local/web.Lock if [ "$UID" -ne 0 ] then echo"must be root can run this script.!" exit fi if [ -f $lockfile ] then echo "script already runing."&&exit else touch $lockfile fi send_msg_to_fetion() { /usr/local/bin/sms -f 138000000 -p password -t 138000000 -m "$date $msg" -d 1 >/dev/null 2>&1 } send_msg_to_fanfou() { curl -u hackcrisman@gmail.com:password -d status="$date $msg" http://api.fanfou.com/statuses/update.xml >/dev/null 2>&1 } server_all_num=${#server_list [*]} i=0 while [ $i -lt $server_all_num ] do server_ip=$(echo ${server_list[$i]}|awk -F':' '{print $1}') server_port=$(echo ${server_list[$i]}|awk -F':' '{print $2}') if curl -m 10 -G http://${server_list[$i]} > /dev/null 2>&1 then status=1 echo "服务器${server_ip},端口${server_port}可以正常访问。" >>$okmsg msg="服务器${server_ip},端口${server_port}可以正常访问。" else if ping -c 1 $server_ip >/dev/null 2>&1 then status=2 echo "服务器${server_ip},端口${server_port}无法访问,但可以Ping 通" >>$errormsg msg="服务器${server_ip},端口${server_port}无法访问,但可以Ping 通" else status=0 echo "服务器${server_ip},端口${server_port}无法访问,且无法Ping 通" >>$errormsg msg="服务器${server_ip},端口${server_port}无法访问,且无法Ping 通" fi fi send_msg_to_fanfou send_msg_to_fetion (( i++)) done rm -rf $lockfile
终端下发送html邮件
准备好邮件内容,格式如下:
To: address@example.com Subject: Subject Content-Type: text/html; charset="gbk" /* You can of course add more header lines if necessary. */ <html> ... your carefully crafted html content ... </html>
保存为mailhtml.html,利用这个命令发送
<code bash>
/usr/sbin/sendmail address@example.com < mailhtml.html
</code>
rrdtool计算网卡发送速率
/opt/rrdtool/bin/rrdtool fetch /var/www/html/cacti/rra/2/130.rrd \ AVERAGE -r 300 -s -5minutes | sed -n '3p' | awk '{print $3}' | \ awk '{printf "%.f\n" ,$1 * 8 / 1000000}'
用shell写代替netstat命令的脚本
#! /bin/sh cat /proc/net/tcp /proc/net/tcp6 2>/dev/null > /tmp/a awk '{print $2,$3,$4}' /tmp/a | awk ' BEGIN { # set fs FS = "[ ]*|:" ; # print header printf("Local-Address Foreign-Address State\n"); } # drop trash message from file tcp && tcp6 ( $0 !~ /local_address/ ){ # get ipv4addr from file /proc/net/tcp if (length($1) == 8) { local_addr_ip4 = strtonum("0x"substr($1,1,2)) ; local_addr_ip3 = strtonum("0x"substr($1,3,2)) ; local_addr_ip2 = strtonum("0x"substr($1,5,2)) ; local_addr_ip1 = strtonum("0x"substr($1,7,2)) ; rem_addr_ip4 = strtonum("0x"substr($3,1,2)) ; rem_addr_ip3 = strtonum("0x"substr($3,3,2)) ; rem_addr_ip2 = strtonum("0x"substr($3,5,2)) ; rem_addr_ip1 = strtonum("0x"substr($3,7,2)) ; } else # get ipv6addr from file /proc/net/tcp6 { local_addr_ip4 = strtonum("0x"substr($1,25,2)) ; local_addr_ip3 = strtonum("0x"substr($1,27,2)) ; local_addr_ip2 = strtonum("0x"substr($1,29,2)) ; local_addr_ip1 = strtonum("0x"substr($1,31,2)) ; rem_addr_ip4 = strtonum("0x"substr($3,25,2)) ; rem_addr_ip3 = strtonum("0x"substr($3,27,2)) ; rem_addr_ip2 = strtonum("0x"substr($3,29,2)) ; rem_addr_ip1 = strtonum("0x"substr($3,31,2)) ; } local_port = strtonum("0x"$2) ; rem_port = strtonum("0x"$4) ; # analyze $5 tcp stat if ( $5 ~ /06/ ) tcp_stat = "TIME_WAIT" else if ( $5 ~ /02/ ) tcp_stat = "SYN_SENT" else if ( $5 ~ /03/ ) tcp_stat = "SYN_RECV" else if ( $5 ~ /04/ ) tcp_stat = "FIN_WAIT1" else if ( $5 ~ /05/ ) tcp_stat = "FIN_WAIT2" else if ( $5 ~ /01/ ) tcp_stat = "ESTABLISHED" ; else if ( $5 ~ /07/ ) tcp_stat = "CLOSE" else if ( $5 ~ /08/ ) tcp_stat = "CLOSE_WAIT" else if ( $5 ~ /09/ ) tcp_stat = "LAST_ACK" else if ( $5 ~ /0A/ ) tcp_stat = "LISTEN" else if ( $5 ~ /0B/ ) tcp_stat = "CLOSING" else if ( $5 ~ /0C/ ) tcp_stat = "MAX_STATES" printf("%d.%d.%d.%d:%d %d.%d.%d.%d:%d %s\n",local_addr_ip1,local_addr_ip2,local_addr_ip3,local_addr_ip4,local_port,rem_addr_ip1,rem_addr_ip2,rem_addr_ip3,rem_addr_ip4,rem_port,tcp_stat); }' | column -t
用dd自动分割大文件脚本
这个脚本调用 dd 直接把输入流输出为多个文件,自动分割大的文件为若干块。
#!/bin/bash #? 检测参数是否正确 if [ -z "$2" -o ! -r "$1" ]; then echo 'Usage: mince [file] [chunk size] " exit 255 fi #? Shell下获取文件大小经典方法 SIZE=`ls -l $1 | awk '{print $5}'` if [ $2 -gt $SIZE ] ;then echo " chunk size is bigger then file size ,don't need to split " exit 254 fi #? 分割. 注意 由于最后一个文件块大小一定会小于CHUNK,必须用 conv=noerror 强制dd生成最后一个文件块. CHUNK=$2 TOTAL=0 PASS=0 while [ $TOTAL -lt $SIZE ]; do PASS=$((PASS+1) echo "Creating $1.$PASS..." dd conv=noerror if=$1 of=$1.$PASS bs=$CHUNK skip=$((PASS-1) count=1 2>/dev/null TOTAL=$((TOTAL+CHUNK)) done echo "Created $PASS chunks out of $1 ."
要重新组合数据块,用下面命令
cat `ls FILENAME.* | sort -n -t . +2` > FILENAME.complete
倒数秒数的shell脚本
for i in $(seq 10 | tac);do echo -en "\aJust shutdown the APP,please wait for a minute ... ${i} ...\r" sleep 1 done echo
实时获取黄金价格并飞信报警
#!/bin/sh TMP="/tmp/.tmpgold" myprice=242 floated=3 USER="shaohy<13396815591@189.cn>" SENDMAIL="/usr/local/sbin/upyun_sendmail.sh" usd="http://hq.sinajs.cn/list=USDCNY"; curl -s -o $TMP $usd usdprice=`awk -F, '{print $2}' $TMP` echo $usdprice url="http://hq.sinajs.cn/list=hf_GC" curl -s -o $TMP $url goldprice=`awk -F, '{print $3}' $TMP` echo $goldprice todayprice=`echo "scale=2; $goldprice*$usdprice/31.1034768"|bc` echo $todayprice sellprice=`echo "scale=2;$todayprice-$myprice"|bc` buyprice=`echo "scale=2;$myprice-$todayprice"|bc` BOOL=`echo "$sellprice>$floated"|bc` if [ $BOOL -eq 1 ];then $SENDMAIL "$USER" "[OK] Sell Gold!" "$todayprice > $myprice" fi BOOL=`echo "$buyprice>$floated"|bc` if [ $BOOL -eq 1 ];then $SENDMAIL "$USER" "[OK] Buy Gold!" "$todayprice < $myprice" fi $SENDMAIL "$USER" "Gold:$todayprice" "$todayprice `date`"
找出swap占用最大的进程
for i in $( cd /proc;ls --color=never|sed -r 's@/@@g'|awk '{if ($0~/^[0-9]/ && $0 >100) print}');do awk '/Swap:/{a=a+$2}END{print '"$i"',a/1024"M"}' /proc/$i/smaps 2>/dev/null; done | sort -k2nr | head -10
#!/bin/bash # Get current swap usage for all running processes # Erik Ljungstrom 27/05/2011 SUM=0 OVERALL=0 for DIR in `find /proc/ -maxdepth 1 -type d | egrep "^/proc/[0-9]"` ; do PID=`echo $DIR | cut -d / -f 3` PROGNAME=`ps -p $PID -o comm --no-headers` for SWAP in `grep Swap $DIR/smaps 2>/dev/null| awk '{ print $2 }'` do let SUM=$SUM+$SWAP done echo "PID=$PID - Swap used: $SUM - ($PROGNAME )" let OVERALL=$OVERALL+$SUM SUM=0 done echo "Overall swap used: $OVERALL"
随机生成密码
< /dev/urandom tr -dc _A-Z-a-z-0-9 | head -c8
获取网卡incoming流量
#!/bin/bash NIC=eth0 RED_COLOR="\\033[1;31m" # red color GRE_COLOR="\\033[32;1m" # green color NOR_COLOR="\\033[0;39m" # normal color SEC=3 while : ; do time=`date +%Y/%m/%d" "%k":"%M":"%S` net_flood=`ifconfig $NIC|sed -n "8"p` rx_before=`echo $net_flood|awk '{print $2}'|cut -c7-` tx_before=`echo $net_flood|awk '{print $6}'|cut -c7-` echo -en $rx_before, $tx_before sleep $SEC net_flood=`ifconfig $NIC|sed -n "8"p` rx_after=`echo $net_flood|awk '{print $2}'|cut -c7-` tx_after=`echo $net_flood|awk '{print $6}'|cut -c7-` echo " -> " $rx_after, $tx_after rx_result=$[(rx_after-rx_before)*8/$SEC/1024/1024] tx_result=$[(tx_after-tx_before)*8/$SEC/1024/1024] echo -n $time echo -e $GRE_COLOR In_Speed: "$rx_result" mbps $RED_COLOR Out_Speed: "$tx_result" mbps $NOR_COLOR sleep $SEC done
探测到DNS的最快机房
ansible -i lists_cun all \ -a "ping -c100 -i0.1 221.6.4.66|awk '/transmitted/{print \$6};/rtt/{split(\$4,a,\"/\");print a[2]}'" \ -f20
软中断分摊到多CPU
#!/bin/sh cpu_num=$(grep -c process /proc/cpuinfo) irq_num=$(awk -F: '($0 ~ "enp[0-9]*" || $0 ~ "eth[0-9]*"){print $1}' /proc/interrupts) i=0 for num in $irq_num do if [[ $i == $cpu_num ]] then i=0 fi echo "obase=16;2^$i" |bc > /proc/irq/$num/smp_affinity let i=i+1 done
禁用CPU C3/C4/C6状态
for i in /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu[0-9]*/cpuidle/state[3-4]/disable;do echo 1 > $i done
解决措施:
目前发现cstate功能和调频功能有耦合,需要使能cstate来解决cpu性能问题,内核参数
intel_idle.max_cstate=0 idle=poll
Linux下快速获取本机外网IP
仅IP:
curl ifconfig.co curl ifconfig.me
IP+地址:
curl ip.fm curl ipinfo.io
更详细:
curl ip-api.com
利用bash构建openbsd ISO系统
#!/bin/sh # Author : MichaelBibby <michaelbibby@gmail.com> # Updated : DIrk Ye <http://www.dirk.sh> # Date : 2006.09.27 # Purpose : Automatic download file sets and create an OpenBSD -release or # -snapshots ISO. # Version : 0.2.2 # Usage : ./mk_openbsd_iso.sh [3.9|4.0|snapshots] [i386|amd64|sparc64] # ChangeLog: # * 0.2.1 --> 0.2.2: # - Changed TMP_ARCHIVE to current work path # - Added some useful packages # - Store tmp files in different directory by architecture # * 0.2 --> 0.2.1: # - Fix the bug when get value of CDROM_FS. # * 0.1 --> 0.2: # - Add function FETCH_SRC to fetch source code and ports tarballs. # - Modify some temp directories and little adjustment. VERSION="$1" # Special OpenBSD version, like 3.9, 4.0, snapshots. ARCH="$2" # Maechine architecture, like i386, amd64. TMP_ARCHIVE="`/bin/pwd`/tmp.$ARCH/openbsd/$VERSION" # Store all openbsd file sets. SRC_ARCHIVE="$TMP_ARCHIVE/$VERSION" # Store source code and ports tarball. SETS_ARCHIVE="$TMP_ARCHIVE/$VERSION/$ARCH" # Store all installation file sets. PKGS_ARCHIVE="$TMP_ARCHIVE/$VERSION/$ARCH/packages" # Store all packages. FETCH_CMD="wget" # Check the following URL to choose a mirror near you: # http://www.openbsd.org/ftp.html MIRROR="ftp://ftp.openbsd.org/pub/OpenBSD" #MIRROR="http://mirror.openbsd.org.cn/ftp" USAGE() { if [ X"$#" != X"2" ]; then echo "USAGE: $0 VERSION ARCH" echo "e.g.: $0 [3.9|4.0|snapshots] [i386|amd64|...]" exit 255 fi } CHECK_APPS() { # Set all nessessary applications into an ARRAY: APPS. APPS_ARRAY="mkisofs $FETCH_CMD" echo "Checking neccessary applications..." for i in $APPS_ARRAY do if [ ! $(whereis "$i") ] then echo "ERROR: $i is not installed, you should installed first" case $i in mkisofs) echo "mkisofs is always included in package 'cdrtools'.";; esac exit fi done } CHECK_DIRS() { # Set all nessessary dir into an ARRAY: DIRS. DIRS_ARRAY="$SETS_ARCHIVE $SRC_ARCHIVE $PKGS_ARCHIVE" echo "Checking neccessary directories..." # Check and create dirs. for dir in ${DIRS_ARRAY} do if [ ! -d "$dir" ]; then echo -ne "\tWARNNING: $dir NOT exist, creating it..." mkdir -p $dir echo "DONE" fi done } # Fetch OpenBSD's installation file sets, like base39.tgz, comp39.tgz. FETCH_SETS() { TMP_OB_FILES_SETS="/tmp/ob_file_sets" # If you want to specify which file sets will be contained in the iso file, # you should comment the following 2 lines, and create '/tmp/ob_file_sets' # manually, and then write the file sets' names in it. Finally, maybe you # want to comment the line following: 'rm -f $TMP_OB_FILES_SETS'. # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ echo "Downloading OpenBSD file sets' index file..." $FETCH_CMD -O $TMP_OB_FILES_SETS $MIRROR/$VERSION/$ARCH/index.txt # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ for i in $(cat $TMP_OB_FILES_SETS) do echo "Downloading file set: $i..." $FETCH_CMD -c -O $SETS_ARCHIVE/$i $MIRROR/$VERSION/$ARCH/$i done rm -f $TMP_OB_FILES_SETS } FETCH_SRC() { # Fetch source code and ports tarball. if [ X"$VERSION" == X"snapshots" ]; then FILE_LIST="ports.tar.gz" else # If you want to download XF4.tar.gz, just append it to $FILE_LIST. FILE_LIST="src.tar.gz sys.tar.gz ports.tar.gz" fi for i in $FILE_LIST do $FETCH_CMD -c -O $SRC_ARCHIVE/"$i" $MIRROR/$VERSION/"$i" done } FETCH_PKGS() { TMP_OB_PKG_SETS="/tmp/ob_pkg_sets" # If you want to specify which packages will be contained in the iso file, # you should comment the following 2 lines, and create '/tmp/ob_pkg_sets' # manually, and then write the packages' name in it. Finally, maybe you # want to comment the line following: 'rm -f $TMP_OB_PKG_SETS'. # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ echo "Downloading OpenBSD package sets' index file..." $FETCH_CMD -c -O $TMP_OB_PKG_SETS $MIRROR/$VERSION/packages/$ARCH/index.txt # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ cat > $TMP_OB_PKG_SETS <<-"EOF" bash-3.1.1p0.tgz cvsup-16.1h-no_x11.tgz g++-3.3.6p1.tgz gcc-3.3.6p1.tgz gmake-3.80p1.tgz lighttpd-1.4.10p1.tgz lsof-4.75p0.tgz mergemaster-1.46p2.tgz pure-ftpd-1.0.20.tgz python-2.4.2p0.tgz sniffit-0.3.7b.tgz snort-2.4.3.tgz stress-0.18.6.tgz tcpstat-1.4.tgz tcptrace-6.2.0p0.tgz tcptraceroute-1.4p1.tgz thttpd-2.25b.tgz vim-6.4.6p1-no_x11.tgz vim-lang-6.4.6p0-no_x11.tgz wget-1.10.2p0.tgz EOF for i in $(cat $TMP_OB_PKG_SETS) do echo "Downloading package: $i..." $FETCH_CMD -c -O $PKGS_ARCHIVE/$i $MIRROR/$VERSION/packages/$ARCH/$i done rm -f $TMP_OB_PKG_SETS } CREATE_ISO() { CDROM_FS=$(basename ${SETS_ARCHIVE}/cdrom*.fs) MKISOFS_CMD="mkisofs -vrlTJV "OpenBSD_${VERSION}_$ARCH" \ -b $VERSION/$ARCH/${CDROM_FS} \ -c boot.catalog \ -o `/bin/pwd`/OpenBSD_${VERSION}_$ARCH.iso $TMP_ARCHIVE" $MKISOFS_CMD } # ----------- SCRIPT MAIN ------------- USAGE "$@" clear echo -e "\n\ \t# --------------------------------------------------------------------------# \t# ------- We recommend you buy OpenBSD's Offical CD sets to support ------# \t# ------- ongoing development of OpenBSD. There are many good reasons ------# \t# ------- to own an OpenBSD CD set: ------# \t# ------- http://www.openbsd.org/faq/faq3.html#BuyCD ------# \t# --------------------------------------------------------------------------# \t# ------- Warnning: Not every platform supports all boot options. For ------# \t# ------- more information, see also: ------# \t# ------- http://www.openbsd.org/faq/faq4.html#Overview ------# \t# --------------------------------------------------------------------------# \t# ------- Note: The ISO file will only contain base installation file ------# \t# ------- sets, so, if you want to include source code/ports and ------# \t# ------- packages in it, please uncomment the function at the end ------# \t# ------- of script, and read the note of function '\$FETCH_PKGS': ------# \t# ------- FETCH_PKGS && \ ------# \t# --------------------------------------------------------------------------# " sleep 10 CHECK_APPS && \ CHECK_DIRS && \ FETCH_SETS && \ FETCH_SRC && \ FETCH_PKGS && \ CREATE_ISO && \ echo "GOOD, ISO has been created:" echo " `/bin/pwd`/OpenBSD_${VERSION}_${ARCH}.iso"
使用iftop监控网络流量
iftop -i eth0 -N -n -B -P iftop -i eth0 -N -n -B -P -t -L 10 -s 10 > /tmp/iftop.log
这个命令可以看到以KB为单位正常流量(KB是小写Kb的8倍),按小写d和大写D后能看到服务器每个端口消耗的总流量
利用ss统计网络包的健康指标
#!/bin/sh state="established" timestamp=`date "+%d/%b/%Y:%X"` tmpfile="z" hostname=$(hostname) ss2 -4itn state $state dport = :80 or sport = :80 or dport = :443 or sport = :433 or sport = :8100 or dport = :8100 | awk '{ if(NR > 1 && $3 !~ /127.0.0.1/ ) { line=$0; getline; if($0~/minrtt/) print line""$0 } }' | awk '{ split($3,src,":"); Saddress=$3; split($4,dst,":"); Daddress=dst[1];Dport=dst[2]; node_type="network-attack"; split($8,a,"[:/]"); split($13,b,"[:/]"); if ($0 ~ /retrans:/){ split($0,c,"retrans:"); gsub("/.*","",c[2]); Retrans=c[2] }else{ Retrans=0 }; if ($0 ~ /send/){ split($0,d,"send"); gsub("bps.*","",d[2]); if(d[2] ~ /K/) { gsub("K","",d[2]); Send=d[2]/1000 } else if(d[2] ~ /M/) { gsub("M","",d[2]); Send=d[2] } else { Send=d[2] } }; print(Daddress,Saddress,a[2],b[2],Retrans,Send) }' | awk '{ a[$2]++;d[$2]=$1;rtt[$2]+=$3;cwnd[$2]+=$4;retrans[$2]+=$5;send[$2]+=$6 }END{ for (i in a){ z=split(i,q,":") nums=0 if (retrans[i]/a[i] != 0) { nums=int(retrans[i]/a[i]+1) } else{ nums=retrans[i]/a[i] } printf("{\ \"Daddress\":\"%s\", \ \"Saddress\": \"%s\",\ \"SPort\": \"%s\",\ \"rtt\": %d,\ \"cwnd\": %d,\ \"Retrans\": %d,\ \"send\": %d,\ \"total\": %d,\ \"line_state\": \"%s\",\ \"type\": \"%s\",\ \"node_type\": \"%s\",\ \"timestamp\": \"%s +0800\",\ \"hostname\": \"%s\"\ }\n", d[i],q[1],q[2],rtt[i]/a[i],cwnd[i]/a[i],nums,send[i]/a[i],a[i],"ESTAB","bbr","network-attack","'$timestamp'","'$hostname'")} }' > $tmpfile.json curl -XPOST http://chopper.x.upyun.com:4000/v2/log/repo/cdn-common -H 'Apikey:1ndT12Jj85UsXQdat2KOMBEiiT28rsIQ' -H "Content-Type:application/json" -T $tmpfile.json -v
macos下批量修改文件名
#!/bin/bash while read f;do dir=`echo $f|awk -F/ '{print $2}'` old=`echo $f|awk -F/ '{print $NF}'` #sed -E:在 macOS 的 BSD sed 中,使用 -E 来启用扩展正则表达式,其效果等同于 GNU sed 的 -r #oldfile=$(echo "$f" | sed -E 's#(\[|\]| )#\\&#g') oldfile=`echo $old | sed -r -n 's# #\\ #gp'` file=`echo $f|awk -F'[-/]' '{print $NF}'` newfile=`echo $file | sed -r -n 's# #\\ #gp'` echo "$dir --- $oldfile --- $newfile" mkdir -p new/$dir cp -a "$dir/$oldfile" new/"$dir/$newfile" done < list
终端在线音乐电台
#!/bin/bash set -euo pipefail HOST="https://lhttp.qingting.fm/live" MP3="64k.mp3" SUPPORTED_FMS=( "清晨音乐台,$HOST/4915/$MP3" "两广音乐之声,$HOST/20500149/$MP3" "上海流行音乐,$HOST/273/$MP3" "浙江音乐调频,$HOST/4866/$MP3" "江苏经典流行音乐,$HOST/4938/$MP3" "AsiaFM 亚洲音乐台,$HOST/4581/$MP3" ) # 全局变量 CURRENT_PID="" SELECTED_NUM="" CURRENT_PLAY_NAME="" MAX_NUM=${#SUPPORTED_FMS[@]} print_radio_info() { echo "节目列表:" for idx in "${!SUPPORTED_FMS[@]}"; do IFS=',' read -r name url <<< "${SUPPORTED_FMS[$idx]}" local num=$((idx + 1)) if [[ "$SELECTED_NUM" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$num" -eq "$SELECTED_NUM" ]]; then printf " \033[31m[%2d] %s\033[0m\n" "$num" "$name" else printf " %2d %s\n" "$num" "$name" fi done } # 播放节目(参数:节目编号) play_radio() { local radio_num="$1" local index=$((radio_num - 1)) IFS=',' read -r radio_name radio_url <<< "${SUPPORTED_FMS[$index]}" if ps -p "$CURRENT_PID" >/dev/null 2>&1; then kill "$CURRENT_PID" >/dev/null 2>&1 wait "$CURRENT_PID" 2>/dev/null fi SELECTED_NUM="$radio_num" CURRENT_PLAY_NAME="$radio_name" mpg123 -q "$radio_url" >/dev/null 2>&1 < /dev/null & CURRENT_PID=$! if ! ps -p "$CURRENT_PID" >/dev/null; then echo -e "播放失败!请检查网络连接或 mpg123 是否安装。" CURRENT_PID="" CURRENT_PLAY_NAME="" SELECTED_NUM="" fi } main_loop() { while true; do clear print_radio_info read -r -p "请输入节目编号( 1-$MAX_NUM )或 q 退出: " user_input if [[ "$user_input" =~ ^[qQ]$ ]]; then echo "正在退出播放器..." if ps -p "$CURRENT_PID" >/dev/null 2>&1; then kill "$CURRENT_PID" >/dev/null 2>&1 wait "$CURRENT_PID" 2>/dev/null fi clear exit 0 fi if ! [[ "$user_input" =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; then echo -n "错误:请输入有效的数字或 q 退出!" sleep 1 continue fi if [[ "$user_input" -lt 1 || "$user_input" -gt "$MAX_NUM" ]]; then echo -n "错误:无效的节目编号!请输入 1-$MAX_NUM 之间的数字" sleep 1 continue fi play_radio "$user_input" done } # 程序入口 play_radio 1 main_loop