目录
Sed编程实战
参考资料
sed(英语“stream editor”的缩写,俗称流编辑器)是Unix常见的命令行程序。
sed 和其它编辑器比如 vi的区别在于,sed按顺序逐行读取文件。然后,它执行为该行指定的所有操作,并在完成请求的修改之后的内容显示出来,也可以存放到文件中。完成了一行上的所有操作之后,它读取文件的下一行,然后重复该过程直到它完成该文件。所以,又称为“行编译器”
sed 用来把文档或字符串里面的文字经过一个或多个正则匹配和编辑命令转换为另一种格式输出。此特性允许你在脚本中使用编辑命令,执行过程中无须人工干预,极大的方便了重复性编辑任务。所以,经常被系统管理员,架构师用来构建系统的强大的利器。
在这里要注意一点,源文件(默认地)保持不被修改。
Sed编辑命令
| 命令 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| p | 打印文本 |
| d | 删除文本 |
| s | 搜索并且替换文本 |
| a\ | 在当前行后面增加文本 |
| c\ | 用新的文本替换当前行 |
| i\ | 在当前行之前插入文本 |
| r | 读取一个文件 |
| w | 写入一个文件 |
| n | 下一行 |
| h | 把模式空间内容保持至缓存区 |
| H | 把模式空间内容添加到缓存区 |
| x | 用模式空间的内容交换固定缓存的内容 |
| G | 把缓存区的内容追加到游标 |
| g | 把缓存区的内容覆盖到游标 |
| q | 直接退出 |
Sed选项
| 选项 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| -e SCRIPT | 把SCRIPT指定的命令加入到在处理输入的时候运行的系列命令。 |
| -f | 把包含在 SCRIPT-FILE 文件中的命令加入到处理输入的时候运行的系列命令之中。 |
| -n | 安静模式。 |
| -V | 打印版本信息然后退出。 |
正则匹配的要点
匹配数字别忘了中括号外面还有一个中括号。
| 缩写 | 具体含义 |
|---|---|
| [:alnum:] | 字母数字 [a-zA-Z0-9] |
| [:alpha:] | 字母 [a-zA-Z] |
| [:blank:] | 空格或制表键 |
| [:cntrl:] | 任何控制字符 |
| [:digit:] | 数字 [0-9] |
| [:graph:] | 任何可视字符(无空格) |
| [:lower:] | 小写 [a-z] |
| [:print:] | 非控制字符 |
| [:punct:] | 标点字符 |
| [:space:] | 空格 |
| [:upper:] | 大写 [A-Z] |
| [:xdigit:] | 十六进制数字 [0-9 a-f A-F] |
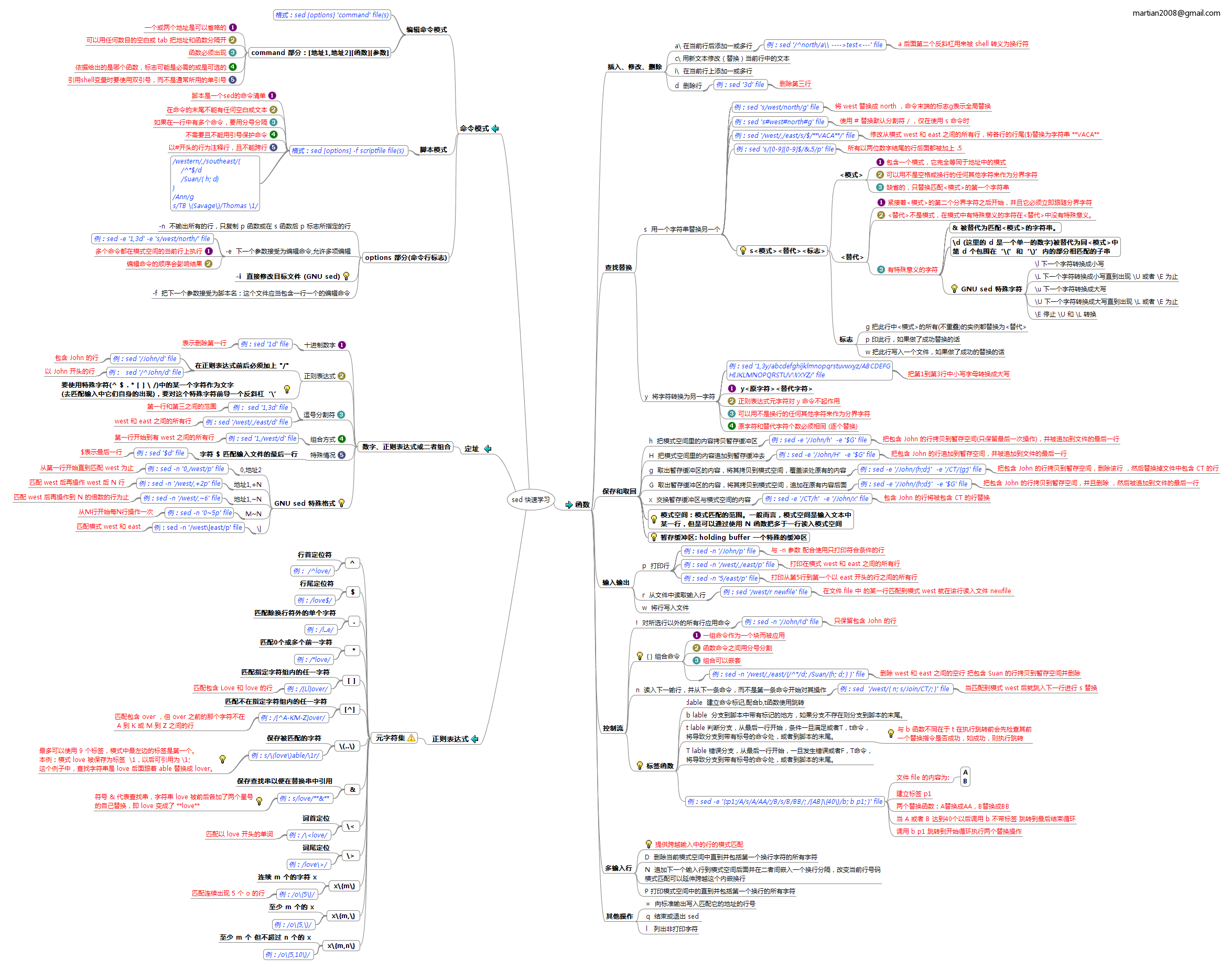
Sed 思维导图
Sed的基本操作
打印包含pattern的行
此命令的作用类似于grep,匹配相关的输出
# sed '/root/p' /etc/passwd|less # sed -n '/root/p' /etc/passwd # sed -n '/^root/p' /etc/passwd # sed -n '/^root/!p' /etc/passwd
删除包括pattern的行
# sed '/root/d' /etc/passwd > a.txt # sed '/^root/d' /etc/passwd > a.txt # sed '/^root/{n;d}' /etc/passwd > a.txt # sed '1,3d' /etc/passwd > a.txt # sed '/^root/,/shutdown/d' /etc/passwd > a.txt # sed -n '/^root/,+3p' /etc/passwd # sed -n '/^root/,~3p' /etc/passwd
替换包括pattern的行
# sed 's/root/shaohy/' a.txt # 一次替换 # sed 's/root/shaohy/g' a.txt # 全部替换 # sed 's/root/&shaohy/g' a.txt # 替换新内容 # sed '1,3s/root/&shaohy/g' a.txt # 指定范围内替换 # sed '1,5s/^/> /gp' a.txt -n # 指定范围内开头添加剂 #### 打印部分内容 = 替换 # sed -r 's:.*=(.*):\1:g' /etc/sysconfig/network # sed -r -n '/HOSTNAME/s:.*=(.*):\1:gp' /etc/sysconfig/network
行追加,修改,插入
# sed -r '/^root/i\>>>> test by geminis' /etc/passwd # sed -r '/^root/a\>>>> test by geminis' /etc/passwd # sed -r '/^root/c\>>>> test by geminis' /etc/passwd
输入文件,输出文件
# sed -r '/^root/r /root/aaa' /etc/passwd > a.txt # sed -r '/^root/w /root/abc' /etc/passwd > a.txt
模式空间与缓存空间的交换
# sed -r -e '/^root/h' -e '/^daemon/H' -e '/sshd/G' /etc/passwd > a.txt # sed -r -e '/^root/h' -e '/^daemon/H' -e '$g' /etc/passwd > a.txt # sed -r -e '/^root/h' -e '/^daemon/H' -e '/zabbix/x' /etc/passwd > a.txt
Sed 实例分析
现在有一段HTML代码,如下:
<h1>Office</h1> <a href="http://www.openoffice.org/" target="_blank">OpenOffice</a> - office suite<br /> <a href="http://www.software602.com/products/pcs/" target="_blank">PC Suite 602</a> - office suite<br />
需要转换成dokuwiki格式,如下:
====Office==== [[http://www.openoffice.org/|OpenOffice]] - office suite [[http://www.software602.com/products/pcs/|PC Suite 602]] - office suite
所以利用sed替换命令,分解完成:
- <h1> </h1> -> ==== - <a href=" -> [[ - " target="_blank"> -> | - </a> -> ]] - -> null - <br /> -> \r\n
最后贴出完整的处理脚本:
sed -r -i \ -e "s:<h1>:====:g" \ -e "s:</h1>:====:g" \ -e 's:<a href=":[[:g' \ -e 's:" target="_blank">:|:g' \ -e 's:</a>:]]:g' \ -e 's: : :g' \ -e 's:<br />:\r\n:g' myfilename.txt
sed 删除空格/空行
sed s/[[:space:]]//g filename 删除空格 sed /^$/d filename 删除空行 sed '/^[\t ]*$/d' spacefile 注意:\t 的後面有一個空白
批量修改文本内容行
for i in `find ./ -name "*.tpl"`;do
sed -i -r '/<title>/s:.*:<title>{{php}}echo WEB_SEO_TITLE{{/php}}</title>:g' $i
done
从文本中读入内容
for file in `find ./ -name "*.tpl"`;do sed -i '/meta/r seo.txt' $file ;done
多网卡策略路由连通方案
# add policy route scripts here sed -i '/NET/d' /etc/iproute2/rt_tables j=0 for i in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth*;do TAB=$(( (++j) * 10 )) DEV=`sed -n '/DEVICE/p' $i|awk -F'=' '{print $2}'` IP=`sed -n '/IPADDR/p' $i|awk -F'=' '{print $2}'` GW=`sed -n '/GATE/p' $i|awk -F'=' '{print $2}'` echo "$TAB $DEV-NET" >> /etc/iproute2/rt_tables ip ro re default via $GW table $TAB ip ru del from $IP prio $TAB ip ru add from $IP table $TAB prio $TAB done ip ro fl ca ip ro fl ca ip ro fl ca
sed交换任意两行
命令:
sed -n 'A{h;n;B!{:a;N;C!ba;x;H;n};x;H;x};p' 文件名
解释:
A、B分别是需要交换的行,C是B-1
其中,A、B、C可以是行号,也可以通过匹配模式,如果是匹配模式,C就需要自己替换为B行的上一行,类似:
</b></font> <code bash> sed -n '/xx/{h;n;/zz/!{:a;N;/yy/!ba;x;H;n};x;H;x};p' 文件名 </code> </html></note> 思路: 对于交换相邻的行 sed -n 'A{h;n;x;H;x};p' 对于交换不相邻的行 sed -n 'A{h;n;:a;N;C!ba;x;H;n;x;H;x};p' 对比发现: <code bash> :a;N;C!ba;x;H;n; 这个部分是多出来的,因此用 B!{..}把这个部分包围起来。 </code> 解释: <code bash> A{…} 遇到A行开始做序列命令 h 把A行放到hold space n 读取一行并替换当前行 :a;N;C!ba 把B行之前的所有行读到pattern space中 x 交换一下,这里hold space 中是 A+1~B-1的内容,pattern space中是A行的内容 H 把A行添加到hold space中,此时,hold space中是A+1~B-1A n 把B行读进pattern space中 x 交换一下,此时,hold space中是B行,pattern space中是A+1~B-1A H 把A+1~B-1A添加到hold space中,此时,hold space中是 BA+1~B-1A x 交换一下,此时pattern space中是 BA+1~B-1A 对于相邻行的情况 B!{:a;N;C!ba;x;H;n} 这个部分将不执行,因为n后,当前行号就是B,因此这个部分跳过。 </code> ==== SED截取某特定两行之间的内容 ==== 从日志中截取某一时刻起到另一时刻的日志,对内容进行分析,用sed来完成吧,截取某特定两行之间的内容: <code bash> sed -n “
:\n:g” \ -e “s:\\\\::g” \ -e “s:
其中,A、B、C可以是行号,也可以通过匹配模式,如果是匹配模式,C就需要自己替换为B行的上一行,类似:
</b></font> <code bash> sed -n '/xx/{h;n;/zz/!{:a;N;/yy/!ba;x;H;n};x;H;x};p' 文件名 </code> </html></note> 思路: 对于交换相邻的行 sed -n 'A{h;n;x;H;x};p' 对于交换不相邻的行 sed -n 'A{h;n;:a;N;C!ba;x;H;n;x;H;x};p' 对比发现: <code bash> :a;N;C!ba;x;H;n; 这个部分是多出来的,因此用 B!{..}把这个部分包围起来。 </code> 解释: <code bash> A{…} 遇到A行开始做序列命令 h 把A行放到hold space n 读取一行并替换当前行 :a;N;C!ba 把B行之前的所有行读到pattern space中 x 交换一下,这里hold space 中是 A+1~B-1的内容,pattern space中是A行的内容 H 把A行添加到hold space中,此时,hold space中是A+1~B-1A n 把B行读进pattern space中 x 交换一下,此时,hold space中是B行,pattern space中是A+1~B-1A H 把A+1~B-1A添加到hold space中,此时,hold space中是 BA+1~B-1A x 交换一下,此时pattern space中是 BA+1~B-1A 对于相邻行的情况 B!{:a;N;C!ba;x;H;n} 这个部分将不执行,因为n后,当前行号就是B,因此这个部分跳过。 </code> ==== SED截取某特定两行之间的内容 ==== 从日志中截取某一时刻起到另一时刻的日志,对内容进行分析,用sed来完成吧,截取某特定两行之间的内容: <code bash> sed -n “
sed -n "/17:29:27/{=;q;}" access.log,sed -n "/17:30:12/{=;q;}" access.logp” access.log
</code>
可以带参数的脚本,使用eval:
三个参数,第一个是文件名,第二个是要找的第一个字符串,第三个是第二个字符串:
<code bash>
#!/bin/bash
a1=sed -n "/$2/{=;q;}" $1
b2=sed -n "/$3/{=;q;}" $1
eval sed -n “${a1},${b2}p” $1
</code>
==== DokuWiKi→Redmine语法转换 ====
<code bash>
#!/bin/sh
SED=“sed -r -i”
FILE=“cdn.txt”
$SED -e “s:======(.)======:\nh1.\1\n:g” \
-e “s:=====(.)=====:\nh1.\1\n:g” \
-e “s:====(.)====:\nh2.\1\n:g” \
-e “s:===(.)===:\nh2.\1\n:g” \
-e “s:==(.)==:\nh3.\1\n:g” \
-e “/<blockquote>/,/<\/blockquote>/s:^:> :g” \
-e “s: - :# :g” \
-e “s:<blockquote>::g” \
-e “s:<\/blockquote>::g” \
-e “s:<html><font.><b>(.)</wrap>:\1:g” \
-e “s:<html><font.>::g” \
-e “s:</font></html>::g” \
-e “s:<b>::g” \
-e “s:</b>::g” \
-e “s::\n:g” \ -e “s:\\\\::g” \ -e “s:
::g” \
- e “s:</note>::g” \
- e “s:
:<pre>:g" \ -e "s:<\/code>:</pre>:g" \ $FILE
sed合并相同行,打标识
sed -r -i '/port.*3130/s@.*@mark_xxx@' $DIR/nginx/app/etc/config.lua sed -r -i 'N;/^(mark_xxx)\n\1$/!P;D' $DIR/nginx/app/etc/config.lua STRING="" if [ ! -z "$KUZAN_UPSTREAM_IMG" ];then xx=$IFS for up in $KUZAN_UPSTREAM_IMG;do IFS=:;read -r ip port <<< "$up" STRING=$STRING"\t\t{ host = \"$ip\", port=$port },\n" done IFS=$xx sed -r -i "/mark_xxx/a\\$STRING\nend_mark_xxx" $DIR/nginx/app/etc/config.lua sed -r -i -e '/mark_xxx/,/end_mark_xxx/{/^$/d}' -e '/mark_xxx/d' $DIR/nginx/app/etc/config.lua fi
苹果macos下的sed用法
grep upyun.com . -r -l | xargs sed -i "" "s@upyun.com@17geek.us@g"