目录
Arduino实验专题
参考资料
- 利用pyFirmata来控制Arduino Arduino With Python: How to Get Started
Arduino编程易用软件
Mixly(基于Blockly)
arduino语法特性
字符串
All of the following are valid declarations for Strings. String stringOne = "Hello String"; // using a constant String String stringOne = String('a'); // converting a constant char into a String String stringTwo = String("This is a string"); // converting a constant string into a String object String stringOne = String(stringTwo + " with more"); // concatenating two strings String stringOne = String(13); // using a constant integer String stringOne = String(analogRead(0), DEC); // using an int and a base String stringOne = String(45, HEX); // using an int and a base (hexadecimal) String stringOne = String(255, BIN); // using an int and a base (binary) String stringOne = String(millis(), DEC); // using a long and a base
数组
int myInts[6]; int myPins[] = {2, 4, 8, 3, 6}; int mySensVals[6] = {2, 4, -8, 3, 2}; char message[6] = "hello";
格式化类型
char msg[50]; snprintf (msg, 75, "hello world #%ld", value); /* float to string 浮点数转换为字符串,用sprintf方式*/ sprintf(msg, "Humidity:%.1f\tTemperature: %.1f", h,t);
安装桌面通讯软件
板卡测试实例
// Pin 13 has an LED connected on most Arduino boards. // give it a name: int led = 13; // the setup routine runs once when you press reset: void setup() { // initialize the digital pin as an output. pinMode(led, OUTPUT); } // the loop routine runs over and over again forever: void loop() { digitalWrite(led, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level) delay(1000); // wait for a second digitalWrite(led, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW delay(1000); // wait for a second }
arduino LED灯系列实验
加强型的红绿灯实验
int red=8; int yellow=9; int green=10; void setup(){ pinMode(red,OUTPUT); pinMode(yellow,OUTPUT); pinMode(green,OUTPUT); } void loop(){ digitalWrite(red,HIGH); delay(5000); digitalWrite(red,LOW); digitalWrite(yellow,HIGH); delay(3000); digitalWrite(yellow,LOW); digitalWrite(green,HIGH); delay(5000); digitalWrite(green,LOW); }
跑马灯实验
int num = 10; int podPin = 0; byte ledPin[] = { 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13}; int ledDelay; int direction = 1; int currentLed = 0; unsigned long changeTime; void setup(){ for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ pinMode(ledPin[i],OUTPUT); } changeTime = millis(); } void loop(){ ledDelay = analogRead(podPin); if((millis()-changeTime) > ledDelay ){ changeLed(); changeTime = millis(); } } void changeLed(){ for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ digitalWrite(ledPin[i],LOW); } digitalWrite(ledPin[currentLed],HIGH); currentLed +=direction; if(currentLed == (num-1)) { direction=-1; } if(currentLed == 0) { direction=1; } }
闪烁灯(sin函数)+报警
int redPin = 3; int greenPin = 5; int yellowPin = 6; float sinVal; int ledVal; int time = 5; void setup(){ for(int x=3;x<=6;x++){ pinMode(x,OUTPUT); } } void loop(){ changeLed(redPin,time); changeLed(greenPin,time); changeLed(yellowPin,time); } void changeLed(int Pin,int time){ for(int x=0;x<180;x++){ float sinVal = sin(x*3.1412/180); int ledVal = int(sinVal*255); analogWrite(Pin,ledVal); delay(time); } }
float sinVal; int toneVal; int ledVal; int ledPin = 4; int tonePin = 8; void setup(){ pinMode(ledPin,OUTPUT); pinMode(tonepin,OUTPUT); } void loop(){ for(int i=0;i<180;i++){ sinVal = (sin(i*(3.1412/180))); toneVal = 2000 + (int(sinVal*1000)); ledVal = int(sinVal*255); tone(tonePin,toneVal); analogWrite(ledPin,ledVal); delay(30); } }
彩色灯(RGB)
float RGB1[3]; float RGB2[3]; float INC[3]; int red,green,blue; int redPin = 4; int greenPin = 5; int bluePin = 6; void setup(){ randomSeed(analogRead(0)); RGB1[0] = 0; RGB1[1] = 0; RGB1[2] = 0; RGB2[0] = random(256); RGB2[1] = random(256); RGB2[2] = random(256); } void loop(){ randomSeed(analogRead(0)); for(int x=0;x<3;x++){ INC[x] = (RGB1[x]-RGB2[x])/256; } for(int x=0;x<256;x++){ red = int(RGB1[0]); green = int(RGB1[1]); blue = int(RGB1[2]); analogWrite(redPin,red); analogWrite(greenPin,green); analogWrite(bluePin,blue); delay(100); RGB1[0] -= INC[0]; RGB1[1] -= INC[1]; RGB1[2] -= INC[2]; } for(int x=0;x<3;x++){ RGB2[x] = random(556)-300; RGB2[x] = constrain(RGB2[x],0,255); delay(1000); } }
最强LED六合一变形
材料准备
接线图
暂省略,后续上电路图
程序设计
byte ledPin[] = {4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; // 定义要用到的led针脚,选取9个输入 int num = sizeof(ledPin); // 统计led灯的数组长度,方便增加或者删除一个灯,不需要变动程序 int ledDelay = 150; // 默认跑马灯的速度为, 150ms int currentLed=0; // 默认从第一个灯开始 int direct; // 定义一个方向变量 int potPin = 0; // 旋钮电位器的模拟量输入针脚,必须要使用Analog In int pbIn = 2; // 选择一个中断信号输入,arduino uno只能使用数字信号的2,3,分别为中断0,中断1 int j = num; int X = 6; // 默认的跑马灯方式 int val=0; unsigned long changeTime; void setup(){ Serial.begin(9600); for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ pinMode(ledPin[i],OUTPUT); // 批量初始化led灯的输出状态 } pinMode(pbIn,INPUT_PULLUP); changeTime = millis(); //attachInterrupt(pbIn, change, RISING);// 当int.0电平改变时,触发中断函数change(改变跑马灯方式),要注意按键防抖 } void change(){ X++; if(X==7) X=1; // 变量累加,如果演示完所有方式,就从第一种开始 } void loop(){ val = digitalRead(pbIn); Serial.println(X); if ( val == 0 ) { ++X; if(X==7) X=1; delay(1000); } ledDelay = analogRead(potPin); // 从旋钮电位器中读值 if((millis()-changeTime) > ledDelay) { switch(X){ case 1: changeLed1();break; case 2: changeLed2();break; case 3: changeLed3();break; case 4: changeLed4();break; case 5: changeLed5();break; case 6: changeLed6();break; default: changeLed1();break; } changeTime = millis(); } } // 第一种: 来回改变方向跑, 同时只有一个灯亮 void changeLed1(){ for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ digitalWrite(ledPin[i],LOW); } digitalWrite(ledPin[currentLed],HIGH); if(currentLed == (num-1)){ direct = -1; } if (currentLed <= 0 ){ direct = 1; } currentLed += direct; } // 第二种: 一路亮过去 void changeLed2(){ if(currentLed == num){ for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ digitalWrite(ledPin[i],LOW); } currentLed = -2; } if (currentLed >= 0 ){ digitalWrite(ledPin[currentLed],HIGH); direct = 1; } currentLed += direct; } // 第三种:三个一组 void changeLed3(){ for(int j=0;j<3;j++){ for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ if(i%3==j){ digitalWrite(ledPin[i],HIGH); } else{ digitalWrite(ledPin[i],LOW); } } delay(ledDelay); } } // 第四种:同时亮,同时灭 void changeLed4(){ for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ digitalWrite(ledPin[i],LOW); } delay(ledDelay); for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ digitalWrite(ledPin[i],HIGH); } } // 第五种:两边往中间跑 void changeLed5(){ for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ digitalWrite(ledPin[i],LOW); } digitalWrite(ledPin[currentLed],HIGH); digitalWrite(ledPin[num-1-currentLed],HIGH); if(currentLed == (num/2)){ direct = -1; } if (currentLed <= 0 ){ direct = 1; } currentLed += direct; } // 第六种:每跑一次就少一个灯 void changeLed6(){ for (int i = 0; i<num; i++) { // 关闭所有LED digitalWrite(ledPin[i], LOW); } digitalWrite(ledPin[currentLed], HIGH); // 点亮当前LED currentLed += direct; // 当前LED号增加direction表示的数值,相当于前进一个LED灯 // 如果达到最后LED灯,则变向 if (currentLed == j) { direct = -1; } if (currentLed == 0) { direct = 1; j--; } if (j == 0) { j = num-1; } }
按键防抖
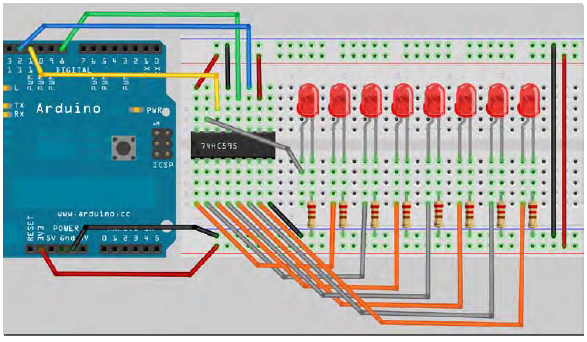
Arduino位移寄存器
74HC595 简单说来就是具有8 位移位寄存器和一个存储器,以及三态输出功能。 这里我们用它来控制8 个LED 小灯。我们为什么要用74HC595 来控制小灯呢?一定会有很多朋友会问这个问题,我想问的是我们要是单纯的用Arduino 控制8 个小灯的话要占用多少个I/O 呢?答案是8 个,但是我们的Arduino 168 有几个I/O 口呢?加上模拟接口也就20 个吧,这8 个小灯占用了太多的资源了,我们用74HC595 的目的就是减少I/O 口的使用数量。用74HC595 以后我们可以用3 个数字I/O 口控制8 个LED 小灯岂不美哉。下面是我们要准备的元器件。
Arduino LCD实验
小学数学语文练习
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> LiquidCrystal lcd(12,11,5,4,3,2); void setup(){ lcd.begin(16,2); } void loop(){ String Xarray[]={ "+","-" }; int Xseed = random(0,2); String direct = Xarray[Xseed]; //mathHomeWork(direct); yuwenHomeWork(); //lcd.print("shao dong jun"); //delay(60000); //lcd.clear(); //lcd.print("chen mei rong"); //delay(60000); } void yuwenHomeWork(){ lcd.clear(); String Yarray[]={ "a","o","e","u","v","d","t","n","b","p","m","f","l","g","k","h","j","q","x","zh","ch","sh","r","z","c","s","y","w","i","ai","ei","ui","ao","ou","iu","ie","ve","er","an","en","in","un","vn","ang","eng","ong","ing" }; int Yseed = 47; int num1 = random(0,Yseed); int num2 = random(0,Yseed); int num3 = random(0,Yseed); int num4 = random(0,Yseed); int num5 = random(0,Yseed); String str = Yarray[num1] + " " + Yarray[num2] + " " + Yarray[num3] + " " + Yarray[num4] + " " + Yarray[num5]; lcd.print(str); delay(2000); } void mathHomeWork(String direct){ lcd.clear(); int num1 = random(0,10); int num2 = random(0,10); int temp; int total; if(direct == "+"){ total = num1 + num2; } else if(direct == "-"){ if(num1 < num2){ temp = num2; num2 = num1; num1 = temp; } total = num1 - num2; } else{ total = 0; } String str1 = String(num1); String str2 = String(num2); String str = str1 + " " + direct + " " + str2 + " = "; lcd.print(str); delay(5000); lcd.clear(); lcd.print(str + String(total)); delay(2000); }
Arduino与web互通
Arduino与串口通讯
const int analogInPin = A0; // Analog input pin that the potentiometer is attached to int sensorValue = 0; // value read from the pot int prevsensorValue = 0; void setup() { // initialize serial communications at 9600 bps: Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { // read the analog in value: sensorValue = analogRead(analogInPin); if (prevsensorValue != sensorValue) { // print the results to the serial monitor: Serial.print("A"); Serial.print(sensorValue); Serial.print("B"); prevsensorValue = sensorValue; } // wait 100 milliseconds before the next loop // for the analog-to-digital converter to settle // after the last reading: delay(100); }
PC端读取串口数据
var SerialPort = require('./lib/node_modules/serialport').SerialPort; var portName = '/dev/tty.usbmodem1411'; var io = require('./lib/node_modules/socket.io').listen(8000); // server listens for socket.io communication at port 8000 io.set('log level', 1); // disables debugging. this is optional. you may remove it if desired. var sp = new SerialPort(portName,{ baudRate: 9600, // this is synced to what was set for the Arduino Code dataBits: 8, // this is the default for Arduino serial communication parity: 'none', // this is the default for Arduino serial communication stopBits: 1, // this is the default for Arduino serial communication flowControl: false // this is the default for Arduino serial communication }); io.sockets.on('connection', function (socket) { // If socket.io receives message from the client browser then // this call back will be executed. socket.on('message', function (msg) { console.log(msg); }); // If a web browser disconnects from Socket.IO then this callback is called. socket.on('disconnect', function () { console.log('disconnected'); }); }); var cleanData = ''; // this stores the clean data var readData = ''; // this stores the buffer sp.on('data', function (data) { // call back when data is received readData += data.toString(); // append data to buffer // if the letters 'A' and 'B' are found on the buffer then isolate what's in the middle // as clean data. Then clear the buffer. //console.log('have raw data: ' + readData); if (readData.indexOf('B') >= 0 && readData.indexOf('A') >= 0) { cleanData = readData.substring(readData.indexOf('A') + 1, readData.indexOf('B')); console.log('have data: ' + cleanData); readData = ''; io.sockets.emit('message', cleanData); } });
各种传感器收集
DIN和DOUT区别
SPI接口需要两条控制线(低电平有效CS和SCLK)和两条数据线(DIN/SDI和DOUT/SDO)。
DIN/SDI数据线为MOSI (主机出,从机入),DOUT/SDO数据线为MISO (主机入,从机出),DIN是从机的数据输入线,DOUT是从机的数据读出线。
DIN数据锁定在SCLK信号的上升沿。在同样的8位周期内,DOUT线上的从机输出数据在SCLK的每个下降沿有效。
1N4148二极管
1N4148是一般的二极管,具有单向导电性,除以上各位所说的功能外,还可作整流用。
如果是串联的那是提高热稳定性的,使稳压值不因工作电流和温度的变化而变化.
如果是反接并联,只能做0.5~0.7V稳压管用了。
LM7805/7806 线性稳压器
以上是常见的型号,使用时输入电压要高于输出电压2-3V以上 例如你使用标称7805的器件,那么他的输出5V是定的,输入电压最好为7.5V以上,要是低于7.5V他就失去无法正常工作了。
LM7805有三根脚(假设图中最下方为1号),1号脚要接输入的正极+,2号脚要接输入负板-
然后是0.33μF/0.47μF电解电容,电容正极接LM7805的1号,负极接LM7805的2号脚。
然后再接0.1μF陶瓷电容,这个无极性,一脚接LM7805的2号,一脚接LM7805的3号脚。
最后,LM7805稳压器的3号脚输出5v(黄线),2号脚是负极(橙色)。并联电容的作用是滤波不是稳压,它的作用原理是负载电流正常时充电到电压等于电池电压,负载电流陡然短时间增加时能从电容中放出一些电荷来弥补电池放电量的不足,对长时间的影响和电池本身电压下降的影响没有作用。
74HC595
74HC595 简单说来就是具有8位移位寄存器和一个存储器,以及三态输出功能。用74HC595 以后我们可以用3个数字I/O口控制8个LED。
int latchPin = 5; int clockPin = 4; int dataPin = 2; //这里定义了那三个脚 void setup () { pinMode(latchPin,OUTPUT); pinMode(clockPin,OUTPUT); pinMode(dataPin,OUTPUT); //让三个脚都是输出状态 } void loop() { for(int a=0; a<256; a++) //这个循环的意思是让a这个变量+1一直加到到256,每次循环都进行下面的活动 { digitalWrite(latchPin,LOW); //将ST_CP口上面加低电平让芯片准备好接收数据 shiftOut(dataPin,clockPin,MSBFIRST,a); //这个就是用MSBFIRST参数让0-7个针脚以高电平输出(LSBFIRST 低电平)是dataPin的参数, //clockPin的参数是变量a,前面我们说了这个变量会一次从1+1+到256,是个十进制数, // 输入到芯片后会产生8个二进制数,达到开关的作用 digitalWrite(latchPin,HIGH); //将ST_CP这个针脚恢复到高电平 delay(1000); //暂停1秒钟让你看到效果 } }